题目就是要求最短路,我们根据数据规模采用Dijkstra+Heap的算法。这里C++如果使用STL中的堆是没有办法过的。
#include <cstdio>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 10000+5;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef pair<string,int> psi;
typedef vector<pii>::iterator iter;
vector<pii> road[MAXN];
vector<psi> city;
int n,dis[MAXN],size;
int heap[MAXN],hash[MAXN];
inline void trylo(int u) {
int tmp = heap[u],i = u;
while (i*2+1<size) {
int j = i*2+1;
if (dis[heap[j+1]]<dis[heap[j]]) j++;
if (dis[heap[j]]<dis[tmp]) {
heap[i] = heap[j];
hash[heap[i]] = i;
i = j;
}
else break;
}
heap[i] = tmp;
hash[heap[i]] = i;
}
inline void tryhi(int u) {
int tmp = heap[u],i = u;
while (i>0) {
int j = (i-1)/2;
if (dis[tmp]<dis[heap[j]]) {
heap[i] = heap[j];
hash[heap[i]] = i;
i = j;
}
else break;
}
heap[i] = tmp;
hash[heap[i]] = i;
}
inline void push(int u) {
heap[size] = u; hash[u] = size++;
tryhi(size-1);
}
inline int htop() {
int ret = heap[0];
hash[heap[0]] = -1;
heap[0] = heap[size-1];
hash[heap[0]] = 0;
size--;
trylo(0);
return ret;
}
int dijkstra(int x,int y) {
memset(dis,127,sizeof(dis));
dis[x] = 0;
size = 0;
memset(hash,-1,sizeof(hash));
push(x);
while (size) {
int u = htop();
for (iter i = road[u].begin(); i!=road[u].end(); ++i) {
int v = i->second;
if (dis[v]>dis[u]+i->first) {
dis[v] = dis[u]+i->first;
if (hash[v]==-1) push(v);
else tryhi(hash[v]);
}
}
}
return dis[y];
}
int main() {
int ncase;
scanf("%d",&ncase);
while (ncase--) {
scanf("%d",&n);
city.clear();
for (int i = 0,m; i<n; i++) {
char _name[16];
scanf("%s%d",_name,&m);
city.push_back(psi(string(_name),i));
road[i].clear();
for (int j = 0,t,c; j<m; j++) {
scanf("%d%d",&t,&c); t--;
road[i].push_back(pii(c,t));
}
}
sort(city.begin(),city.end());
int query;
scanf("%d",&query);
while (query--) {
char _na[16],_nb[16];
scanf("%s%s",_na,_nb);
int ia = lower_bound(city.begin(),city.end(),psi(string(_na),0))->second;
int ib = lower_bound(city.begin(),city.end(),psi(string(_nb),0))->second;
printf("%d\n",dijkstra(ia,ib));
}
}
return 0;
}
Your program in C++ from 2010-03-20 04:16:58 ran for 2.66 seconds and used 7020 KB of memory.
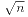 范围内的质数,然后对指定的区间再使用筛法就可以了。不需要特别的优化。
范围内的质数,然后对指定的区间再使用筛法就可以了。不需要特别的优化。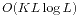 。
。